Python Sets
Sets
Sets are used to store multiple items in a single variable. They are similar to other datatypes like tuples and lists.
Sets are created using curly brackets { }.
Sets are immutable data types, meaning they cannot be edited after creation.
Unordered and Immutable
Sets are unordered and do not have a definite order. They are also unindexed and immutable.
This means you cannot change individual elements of a set, but you can add or remove items.
Duplicates are Not Allowed
Sets do not allow duplicate elements. If there are identical elements, they will be considered the same.
Example
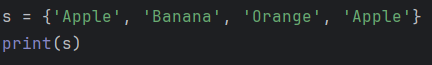
Output
{'Apple', 'Banana', 'Orange'}
In sets, True and 1 are considered to be the same, and False and 0 are considered the same.
Example 1
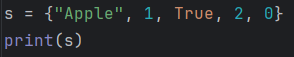
Output
{0, True, 2, 'Apple'}
Example 2
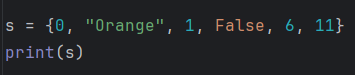
Output
{0, 1, 6, 'Orange', 11}
Set Length
The length of a set is the number of elements it contains, and it can be determined using the len() function.
Example
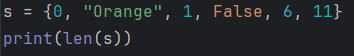
Output
5
The set() Constructor
The set() constructor can be used to create a set from a sequence (like a list or tuple).
Example
Output
{96, 97, 98, 99}