HTML Block-level & Inline Elements
In HTML, elements are categorized into two main types based on how they behave and interact with other elements: block-level elements and inline elements.
Block-Level Elements:
Block-level elements typically start on a new line and occupy the full width available to them by default. They create "blocks" of content. Some common block-level elements include:
-
<div>A generic container for grouping elements and applying styles -
<p>Represents a paragraph of text. -
<h1>to<h1>Headings of various levels. -
<ul>,<ol>,<li>Unordered and ordered lists with list items. -
<table><thead><tbody><tr><th><td>Elements for defining tables and their parts. -
<form><fieldset><legend><input><button>Form-related elements. -
<header><footer><section><article><nav>HTML5 semantic elements for structuring content.
Example of Block-Level Elements:
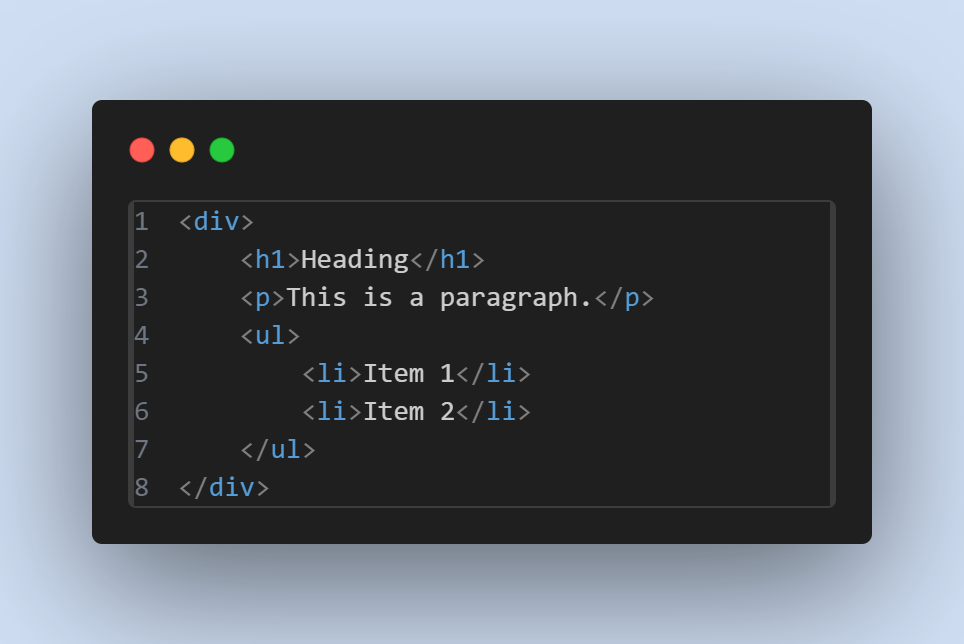

Inline Elements:

Inline elements do not start on a new line and only occupy as much width as necessary. They typically flow within the content and are often used within block-level elements. Some common inline elements include:
-
<span>A generic inline container for text and other inline elements. -
<a>Creates hyperlinks. -
<strong><em><b><i>Text formatting elements for emphasis and style. -
<img>, <br>, <input>, <button>, <label>, <select>, <textarea>, <cite>, <code>, <small>, <sup>, <sub>, <time>, <abbr>, <kbd>, <var>, <mark>, <q>, <s>, <u>, <del>, <ins>Various inline elements used for specific purposes.

Differentiating Block vs Inline :
- Behavior: Block-level elements start on a new line and take up the full width available, whereas inline elements do not start on a new line and only take up as much width as necessary.
- Default Styling: Block-level elements often create visible blocks of content, making them suitable for structuring large parts of a webpage, while inline elements are more useful for styling smaller parts or adding decorations within text.
- Usage:Block-level elements are commonly used for major structural elements of a webpage, such as sections, paragraphs, lists, and forms. Inline elements are typically used for text-level semantics and inline stylistic control.