HTML HEAD
The <head>
element is crucial for defining metadata and linking resources that are essential for the proper functioning and
styling of a webpage.
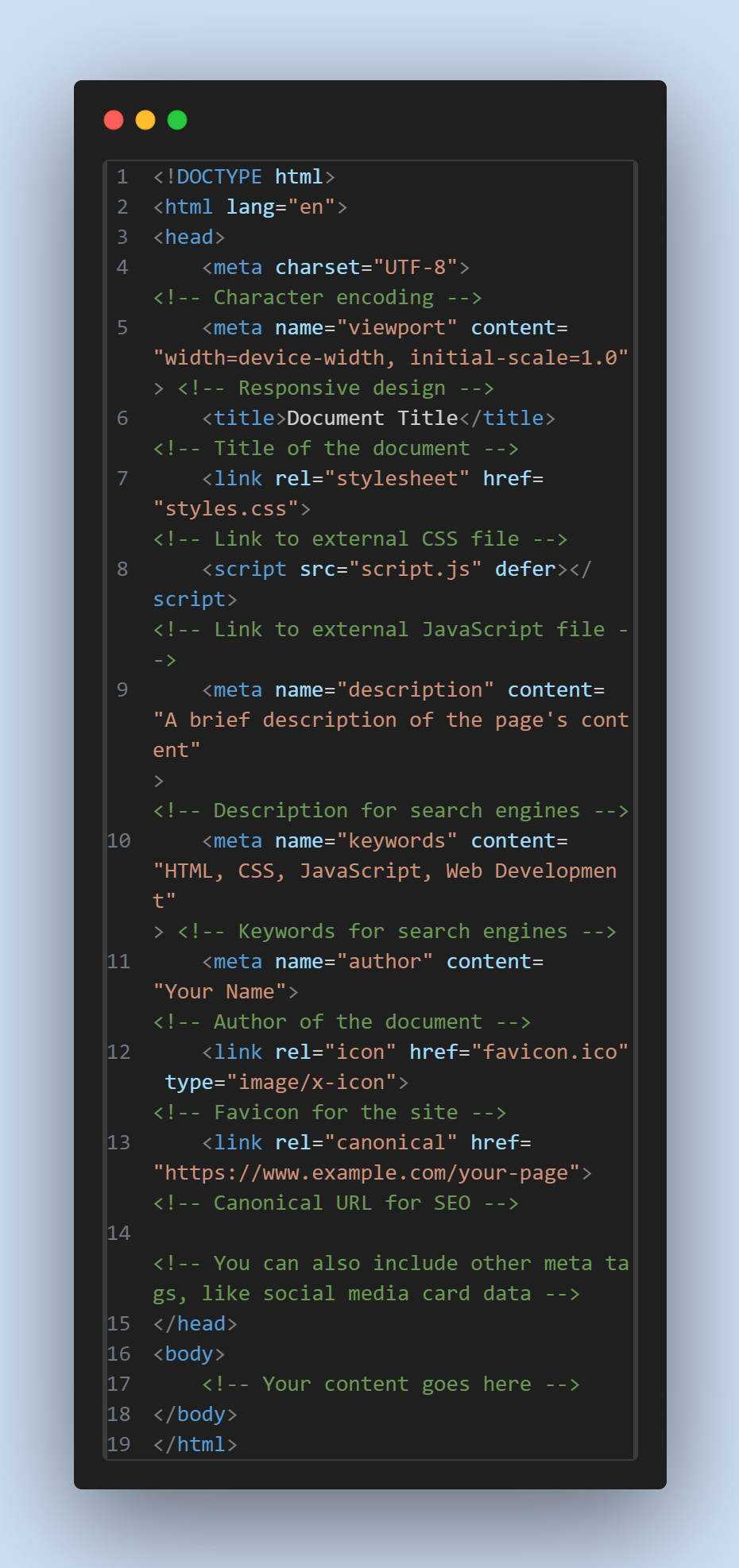
The <head>
element is crucial for defining metadata and linking resources that are essential for the proper functioning
and
styling of a webpage.
-
<meta charset="UTF-8">: Specifies the character encoding for the document, usually UTF-8, which supports a wide range of characters. -
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"">: Helps with responsive design by setting the viewport width to match the device’s width. -
<title>: Sets the title of the webpage, which appears in the browser tab and search engine results. -
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">: Links to an external CSS stylesheet that styles the page. -
<script src="script.js" defer></script>: Links to an external JavaScript file. The defer attribute ensures the script executes after the HTML is fully parsed. -
<script src="script.js" defer><script>: Links to an external JavaScript file. The defer attribute ensures the script executes after the HTML is fully parsed. -
<meta name="description" content="...">: Links to an external JavaScript file. The defer attribute ensures the script executes after the HTML is fully parsed. -
<meta name="keywords" content="...">: Lists keywords relevant to the page content. Note that this is less significant for SEO nowadays. -
<meta name="author" content="...">: Specifies the author of the document. -
<link rel="icon" href="favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon">: Sets the favicon for the site, which appears in the browser tab. -
<link rel="canonical" href="...">: Helps prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the preferred URL for the page.