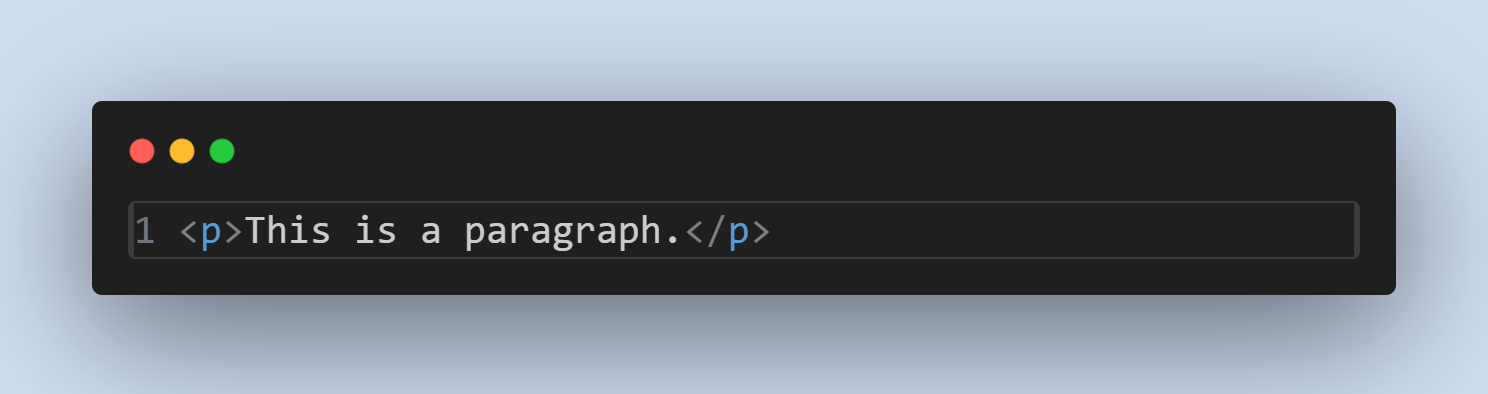
HTML Elements
Understanding HTML Elements
HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML documents. They consist of a starting tag, content, and an ending tag.
Basic Structure of an HTML Element
An HTML element consist of
Start Tag: Marks the beginning of the element.
Content: The information or text enclosed within the tags
End Tag: Indicates the end of the element
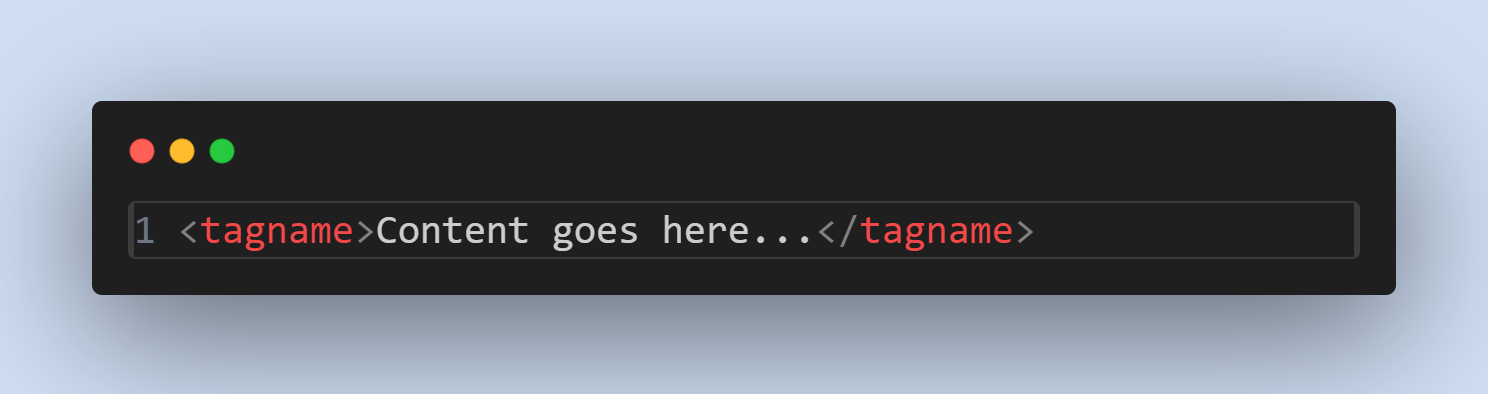
General Syntax:
Example :
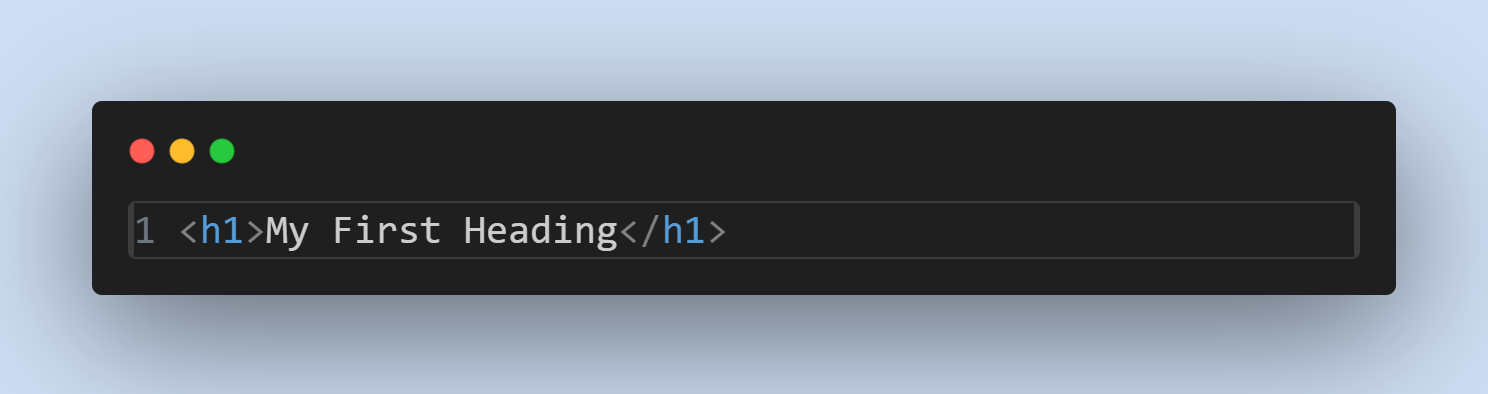
- Heading Element:
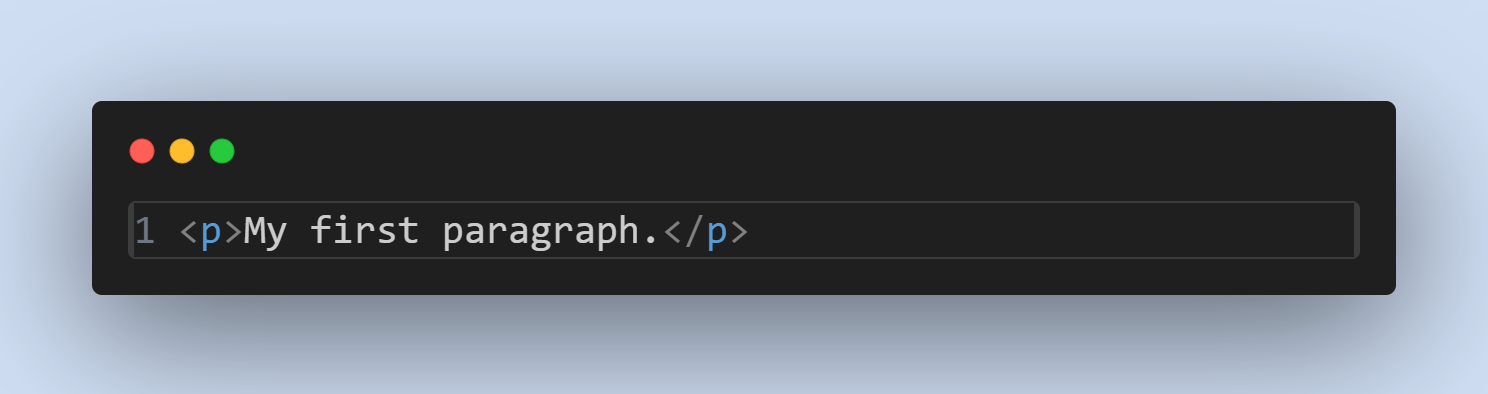
- Paragraph Element:
Components :
- Start Tag:
<h1> - Element Content: My First Heading
- End Tag:
</h1>
Empty Elements:
Some HTML elements, such as <br>, do not have any content and
therefore do not require an end tag. These are known as empty
elements.
Nested HTML Elements
HTML elements can be nested, meaning that an element can contain other elements. This nesting forms the structure of an HTML document.
Example:
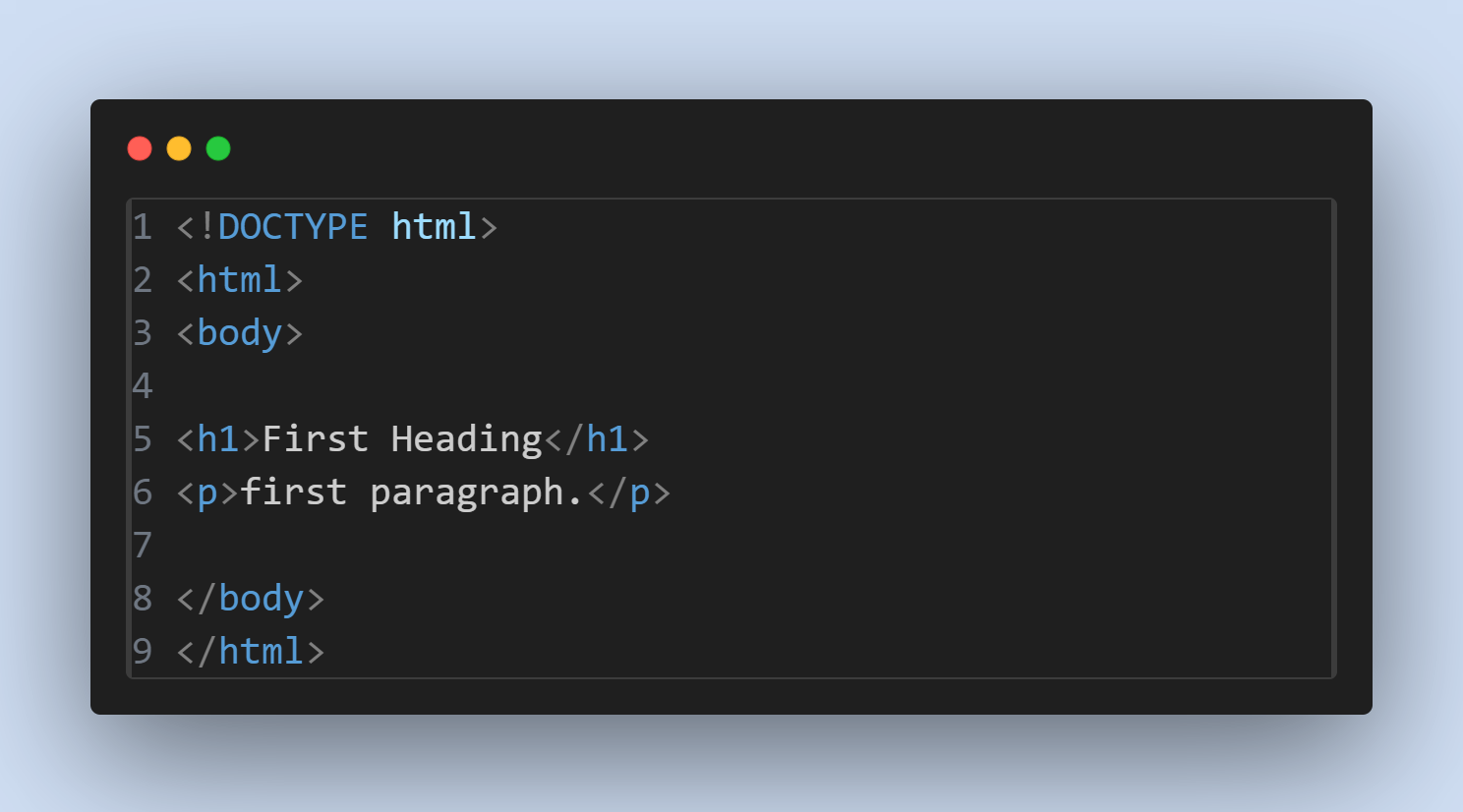
Explanation
<html>Element: The root element that encompasses the entire HTML document.- Start Tag:
<html> - End
Tag:
<html> <body>Element: Defines the main content of the document.- Start
Tag:
<body> - End Tag:
</body> <h1>Element: Represents a top-level heading.- Start
Tag:
<h1> - End Tag:
</h1> <p>Element: Defines a paragraph.- Start
Tag:
<p> - End Tag:
</p>
Importance of End Tags
Although some HTML elements may appear correctly without end tags, it’s crucial to include them to avoid unexpected issues.
Example :
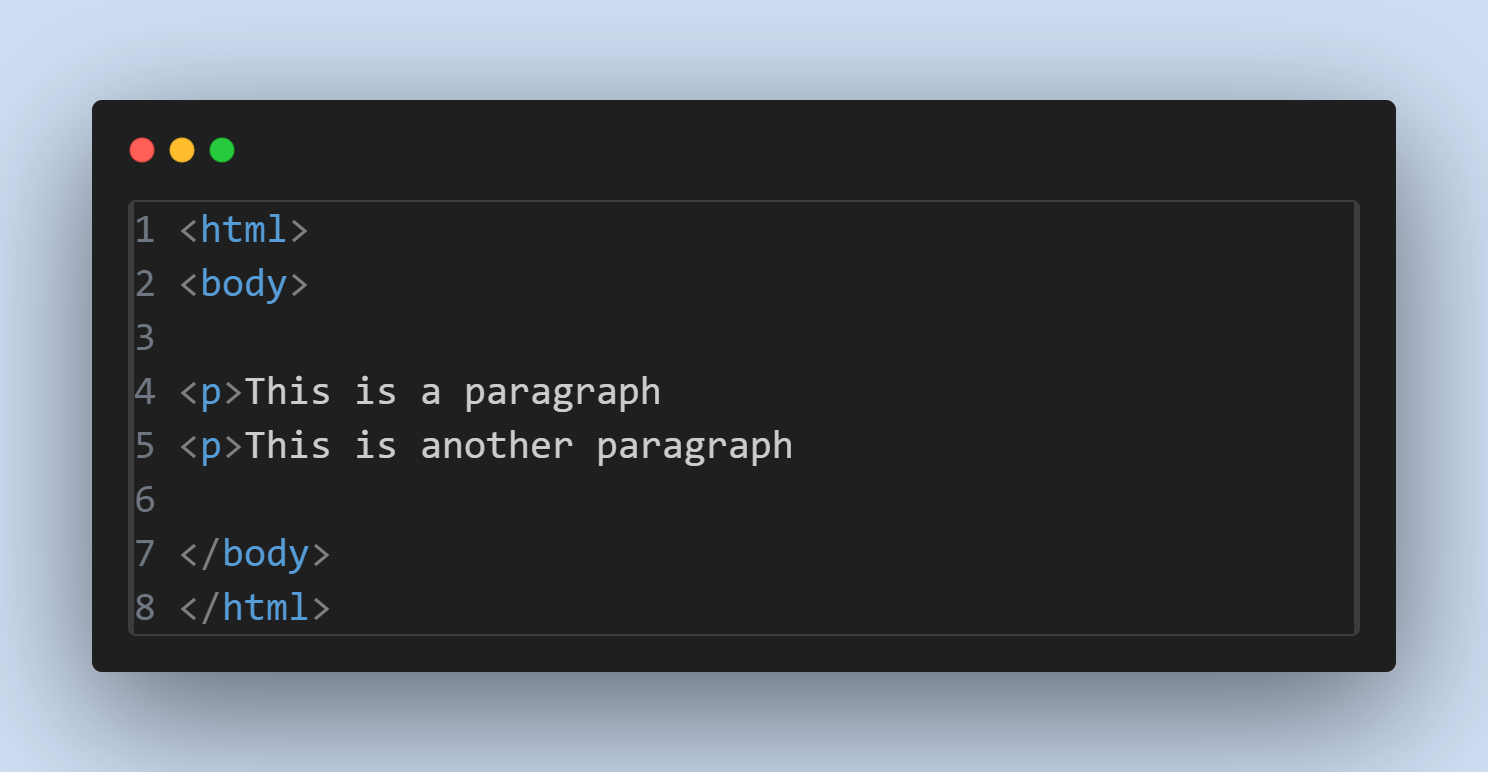 Note: Omitting end tags can lead to unpredictable results and should be avoided.
Note: Omitting end tags can lead to unpredictable results and should be avoided.
Empty HTML Elements
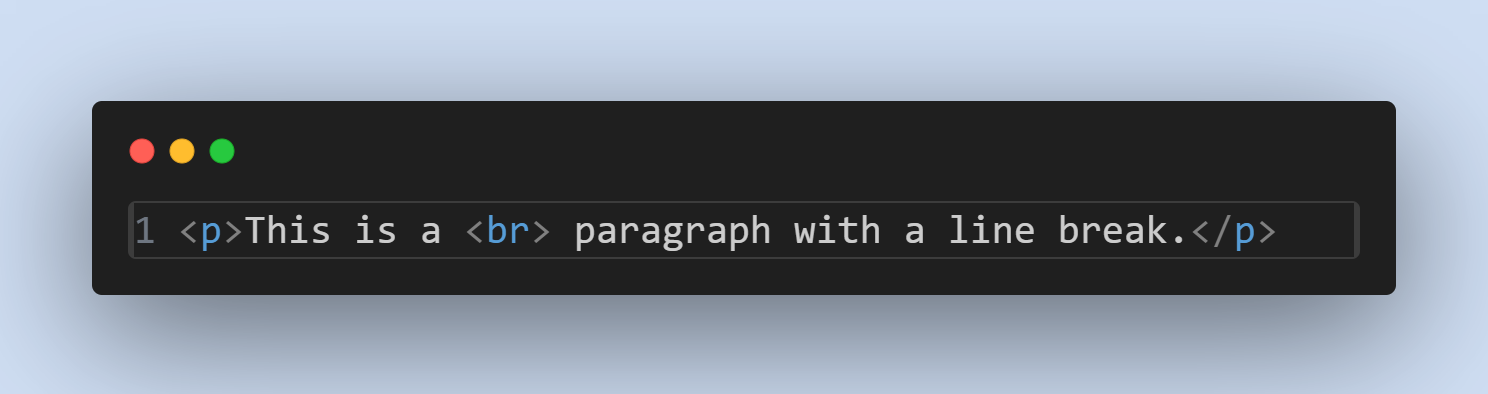
Elements with no content are known as empty elements and do not have end tags. For example:
- Line Break Element
<br>
Case Sensitivity in HTML
HTML tags are not case-sensitive. For instance, <p> and </p>
are
interpreted the same way. Although HTML does not require lowercase tags, using lowercase is
recommended
for consistency and is mandatory for XHTML documents.
Practice Like :
- Use lowercase for HTML tags, as demonstrated