HTML Id and Class
The
<id> and <class> are attributes used to uniquely identify and style
elements on a webpage.
The `id` attribute specifies a unique identifier for an HTML element. Each `id` value must be unique within the HTML document. It is typically used to identify a specific element so that it can be targeted with CSS or JavaScript.
Syntax:
The id attribute is added to an HTML tag like this
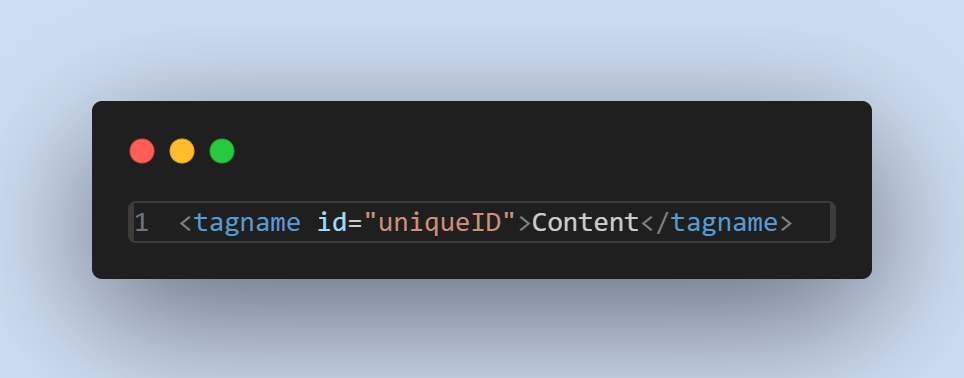
- Example :
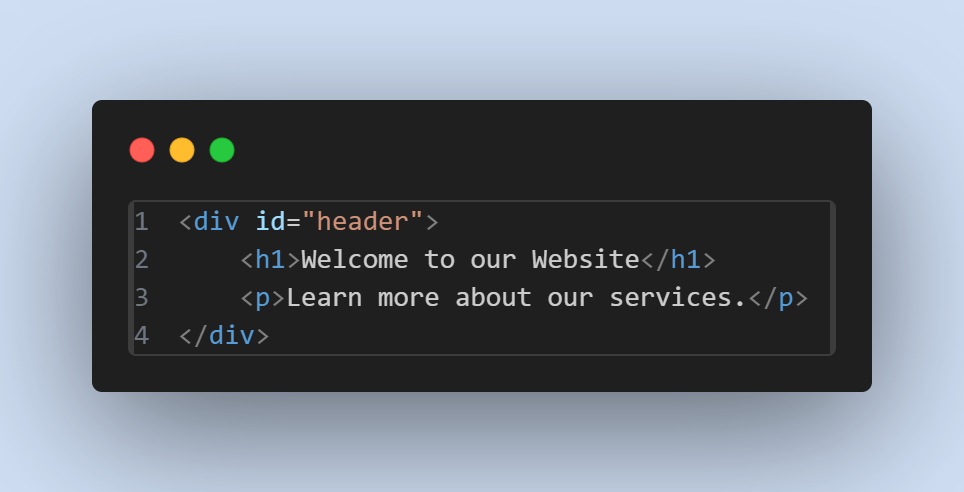
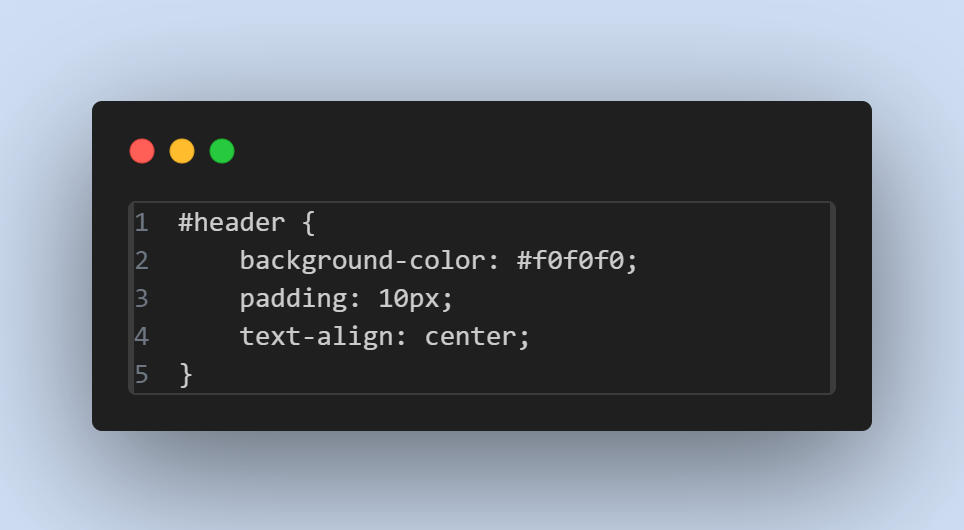
- Usage in CSS :
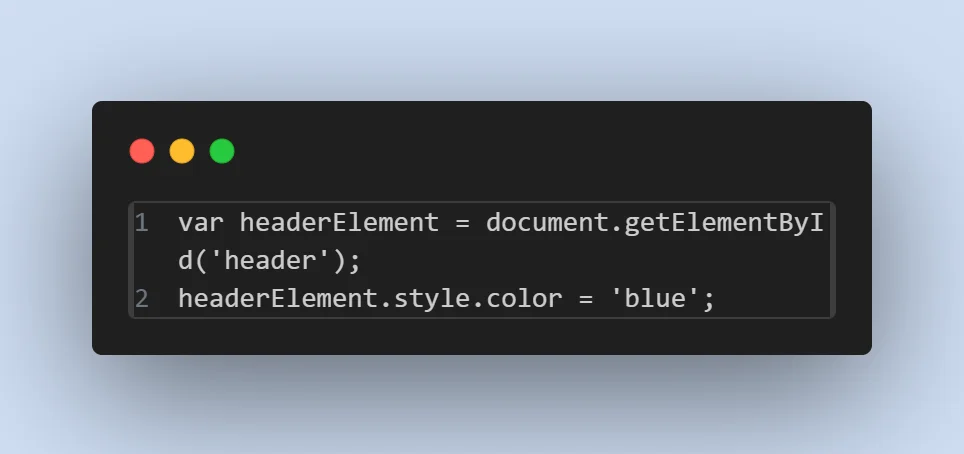
- Usage in JavaScript :
The class attribute in HTML allows multiple elements to share the same class, making it easy to apply
consistent styles or behaviors. You can assign one or more class names to an element, separated by spaces.
For instance,<div class="box highlight" >
applies both box and highlight styles to the element.
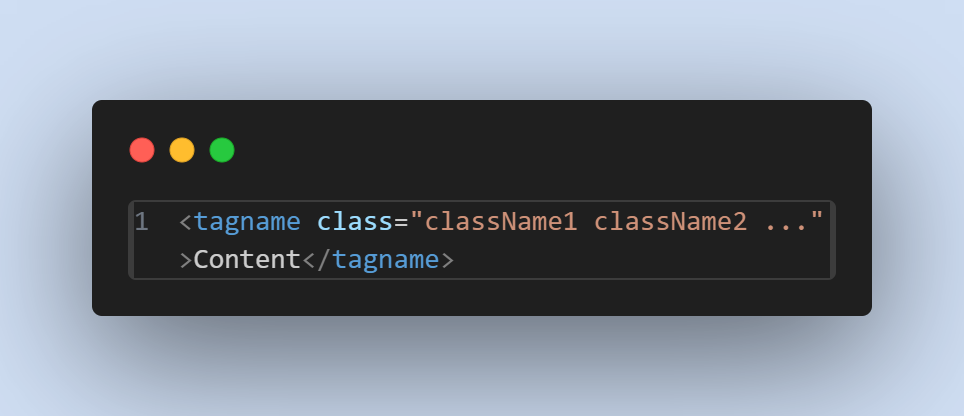
Syntax:
The class attribute can be applied to multiple elements and can include multiple class names separated by spaces.
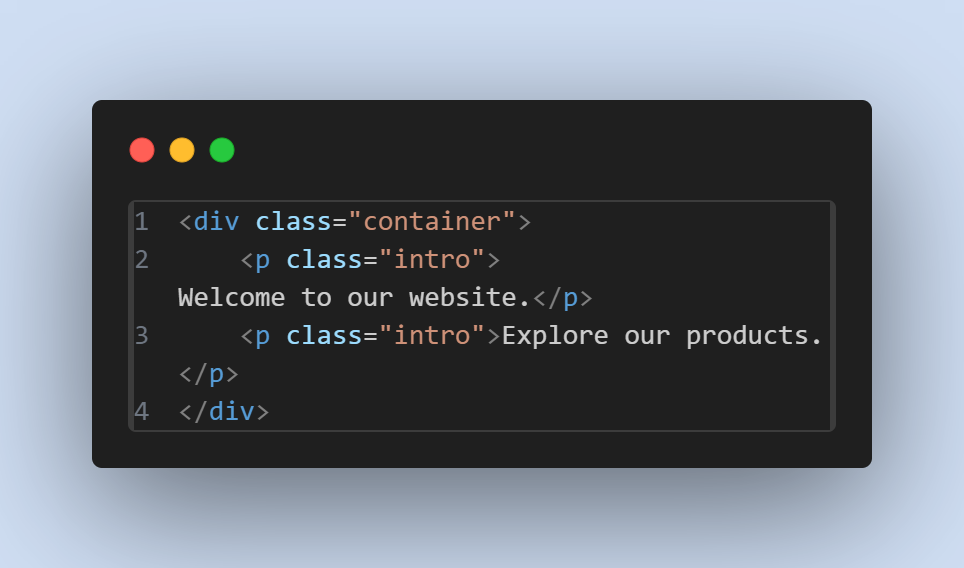
- Example :
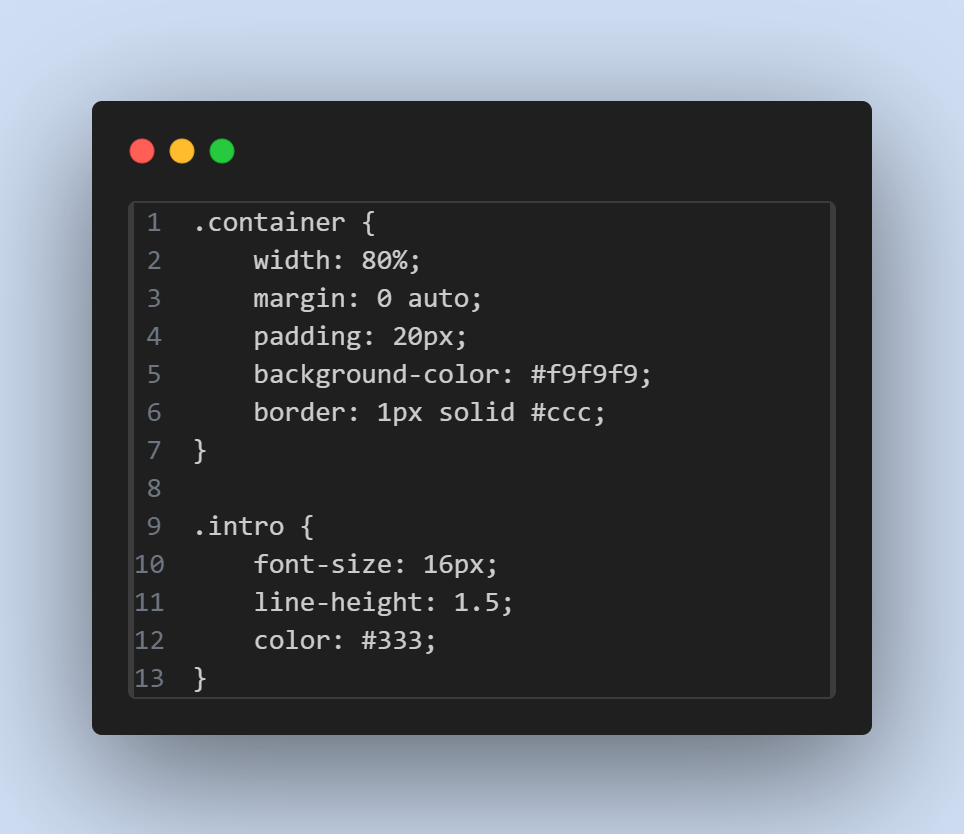
- Usage in CSS :
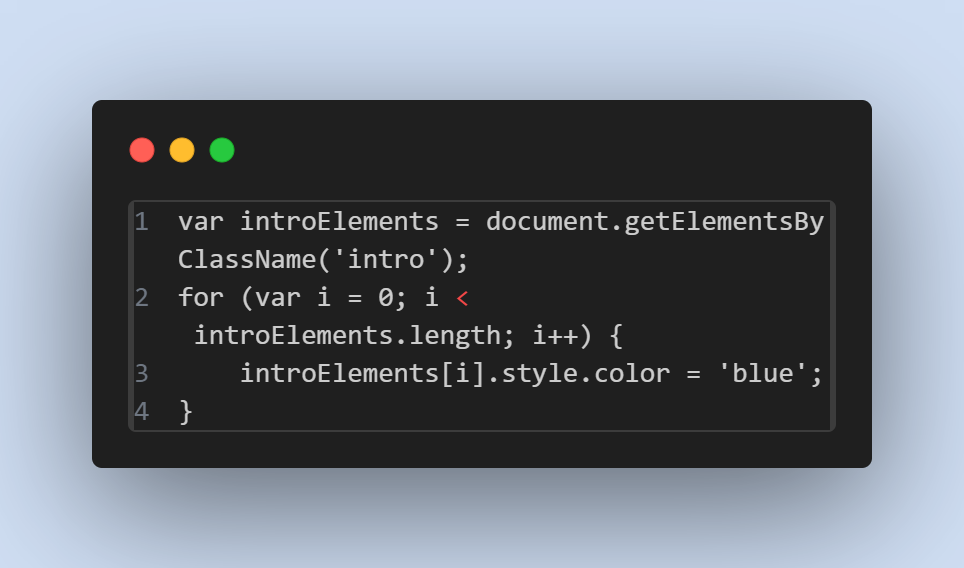
- Usage in JavaScript :
- Uniqueness: id must be unique within the document, whereas class values can be reused across multiple elements.
- Specificity: In CSS, an id selector has higher specificity than a class selector, meaning that styles applied with id selectors will override those applied with class selectors if there’s a conflict.