HTML Div Elements
The
<div> element in HTML is a fundamental building block used for structuring and
organizing
content within a web page.
It is a block-level container that does not carry any specific semantic meaning but allows developers to
group
together elements and apply styles or scripts to them collectively.
Basics of Div
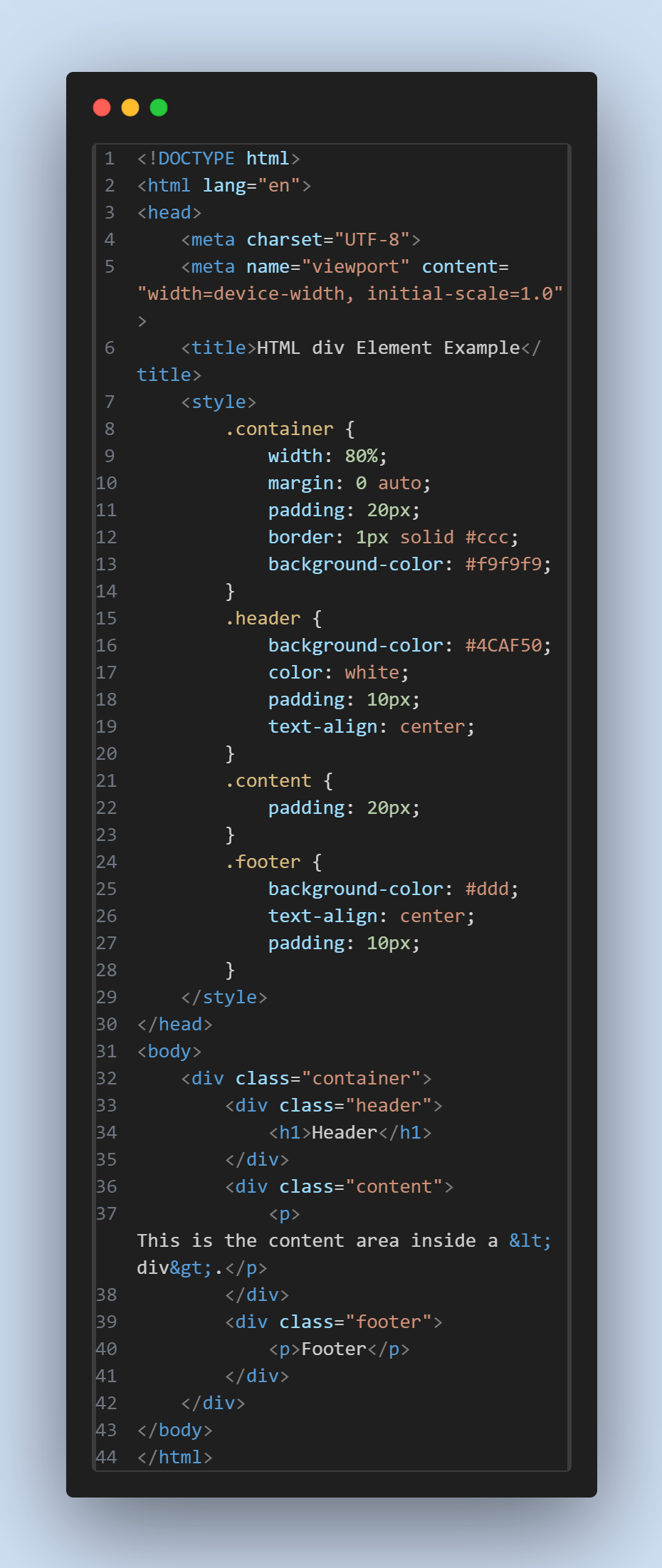
Here's a simple example demonstrating the use of <div>

Explanation :
-
<div class="container">This<div>serves as the main container for the entire content of the webpage. It is styled using CSS to have a specific width, margin, padding, border, and background color. -
.header, .content, .footer:
These are
<div>elements inside the .container<div>, each serving a specific section of the webpage (header, content, and footer). They are styled differently using CSS classes to visually differentiate them.
Key Points
-
Container:
<div>is commonly used as a container to group and organize other HTML elements. -
Styling:
CSS can be applied to
<div>elements and their classes to control their appearance, layout, and behavior. -
Structure:
<div>elements do not have any inherent semantic meaning, so they are often used in conjunction with more semantic HTML5 elements like<header><footer><section>and<article>to structure content. -
Scripting:
JavaScript or libraries like jQuery often manipulate
<div>elements to add dynamic behavior to web pages.